Unlocking Data Intelligence in the Manufacturing Industry
Research has consistently shown that today’s executives openly highlight the need for their organizations to be more data driven – but the data must be highly reliable before you can leverage it in decision making. With a broad and growing focus on leveraging data to drive business value, data intelligence has emerged as a critical area for attention and investment. Think of data intelligence like business intelligence. While the goal of business intelligence is to better understand the business, the goal of data intelligence is to better understand the business’s data. Business intelligence done well and at scale is challenging without data intelligence.
First coined by IDC, data intelligence is a key factor that enables organizations to transition from simply possessing data to leveraging that data to drive actual business value by answering important questions about their data:
- Where is it and where did it come from?
- Who is using it?
- Is it important and why?
- Can we understand it?
- Can we trust its quality?
- Can we use it?
Strengthening these data intelligence capabilities can help organizations build trust around their data, but with so much to do, where should you start?
Challenges We’re Seeing
For the industrial and manufacturing sector, the most important challenges include:
- Data variety and complexity: The data generated from Internet of Things (IoT) devices can be highly diverse and complex, including data from sensors, machines and other devices. This data may be stored in different formats, making it difficult to aggregate and consolidate.
- Data volume: IoT devices are constantly generating vast amounts of data that humans rarely lay their eyes upon, making it challenging to process, store and govern the data efficiently.
- Data quality: Regulated industries will prioritize data integrity and compliance, but also need to check the data is fit for use to ensure analytics are accurate and IoT investments are justified. Manufacturing data quality depends on reliable instrumentation which includes selecting the right sensors, setting the appropriate thresholds, and monitoring for sensor degradation/wear.
Reliable data is a pre-requisite for any asset health, production or energy monitoring use case.
- Data privacy and security: According to IBM, the manufacturing industry was the top threatened industry in 2022. Besides being a prime target for IP theft, this industry is known for frequently transferring confidential data across organizations. This means that a data breach in one organization could potentially impact another. Failures in this area may put a company, its suppliers/partners or even its customers at risk.
- The gap between Information Technology (IT), Operational Technology (OT) and Engineering Technology (ET): IDC notes that Industry ecosystems are generating value through operational data exchange, but this requires appropriate platforms, infrastructures and applications that support use cases. Advancing intelligent devices and software demand tighter IT/OT integration for deeper insights. ET must be a part of the convergence, as virtual modeling tools are now vital for decision-making.
The Rise of Industrial DataOps
While process historians have been employed to overcome certain industry challenges, limitations persist. These include difficulties in handling diverse data types, scaling to accommodate increasing data volumes, robustly integrating data sources, and effectively managing real-time, batch, and analytical processing alongside data governance.
Many have called for a methodology that enhances the operational practices of data experts and supports the shift toward the data-focused enterprise.
The principles, practices, processes and technologies that enable effective data use and improved data-driven decision-making have come to be known as “DataOps”
The term was coined as early as 2014, and quickly gained traction following the surge and early successes of DevOps. Modern Industrial DataOps tools recognize that domain experts and data scientists need simple access to complex industrial data to solve tough problems that drive transformational outcomes in productivity, quality and sustainability. This solution accelerates the journey to scalable and sustainable digital transformation.
Industrial DataOps tools are geared to enable data collaboration and bridge the gap between IT systems, operational data and engineering data – Facilitating contextualization and integration between the different kinds of data in this exchange (structured, unstructured and everything in between) –, and handling, processing and storing large volumes of data.
Achieving data intelligence is possible through DataOps. In fact, Gartner predicts that by 2025, a data engineering team guided by these practices and tools will be 10 times more productive than teams that do not.
Getting Started with Your IT and OT Data Strategy: A Five-Pillar Approach
To embark on a successful data strategy, a strong foundation is crucial. A well-structured approach, centered around five key pillars, can help you navigate the complexities of data enablement.
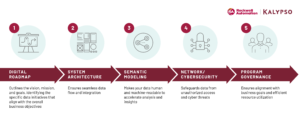
- Digital Roadmap: A clear digital roadmap provides the strategic direction. It outlines the vision, mission, and goals, identifying the specific data initiatives that align with the overall business objectives. The roadmap should prioritize projects, allocate resources, and establish a timeline for implementation.
- System Architecture: A robust system architecture ensures seamless data flow and integration. It involves designing and implementing a data infrastructure that supports the organization's needs. This includes leveraging Modern Industrial DataOps tools.
- Semantic Modeling: A well-defined semantic model provides a shared understanding of data. It involves creating a conceptual data model that defines entities, attributes, and relationships. By establishing a common data language based on business context, semantic modeling makes your data human and machine readable to accelerate analysis and insights.
- Network/Cybersecurity: A secure network infrastructure is essential to protect sensitive data. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures, such as firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption safeguards data from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Program Governance: Effective program governance ensures alignment with business goals and efficient resource utilization. It involves establishing governance structures, defining roles and responsibilities, and implementing change management processes. Regular monitoring and evaluation are crucial to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
The Bottom Line
Drawing inspiration from the data enablement practices that have emerged within the IT domain over the past decade, particularly DevOps, manufacturing teams can leverage and adapt existing data governance frameworks to address the unique challenges of the Operational Technology (OT) environment.
By embracing Industrial DataOps principles, founded upon a robust data governance foundation, organizations can streamline data discovery, enhance data understanding, and ultimately unlock significant business value. This translates to tangible improvements such as enhanced operational efficiency, improved product quality, reduced downtime, and the agility to swiftly adapt to evolving market demands.
Fostering a culture of data-driven decision-making through a well-executed Industrial DataOps strategy empowers manufacturers to harness the full potential of their data, driving innovation across the entire manufacturing value chain and securing a competitive advantage.


